AI Agents and Agentic Security: The Next Frontier in Enterprise Automation
- English
- Español
- 中文
- हिन्दी
- Português
- Français
- Deutsch
- 日本語
- 한국어
Traditional automation tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) have long served as the backbone of enterprise workflows. These systems, designed to automate repetitive tasks and connect disparate software tools, have delivered undeniable value. However, their inherent limitations are becoming increasingly evident. They require significant manual setup, often break when systems change, and struggle to handle unstructured data such as documents, emails, or images.
Enter AI agents — a revolutionary leap from static, rule-based automation to intelligent, adaptable systems. AI agents promise to overcome the constraints of traditional tools, paving the way for smarter, more efficient enterprise automation. An excellent breakdown of their significance can be found in the insightful Menlo Ventures article “Beyond Bots: How AI Agents Are Driving the Next Wave of Enterprise Automation”.
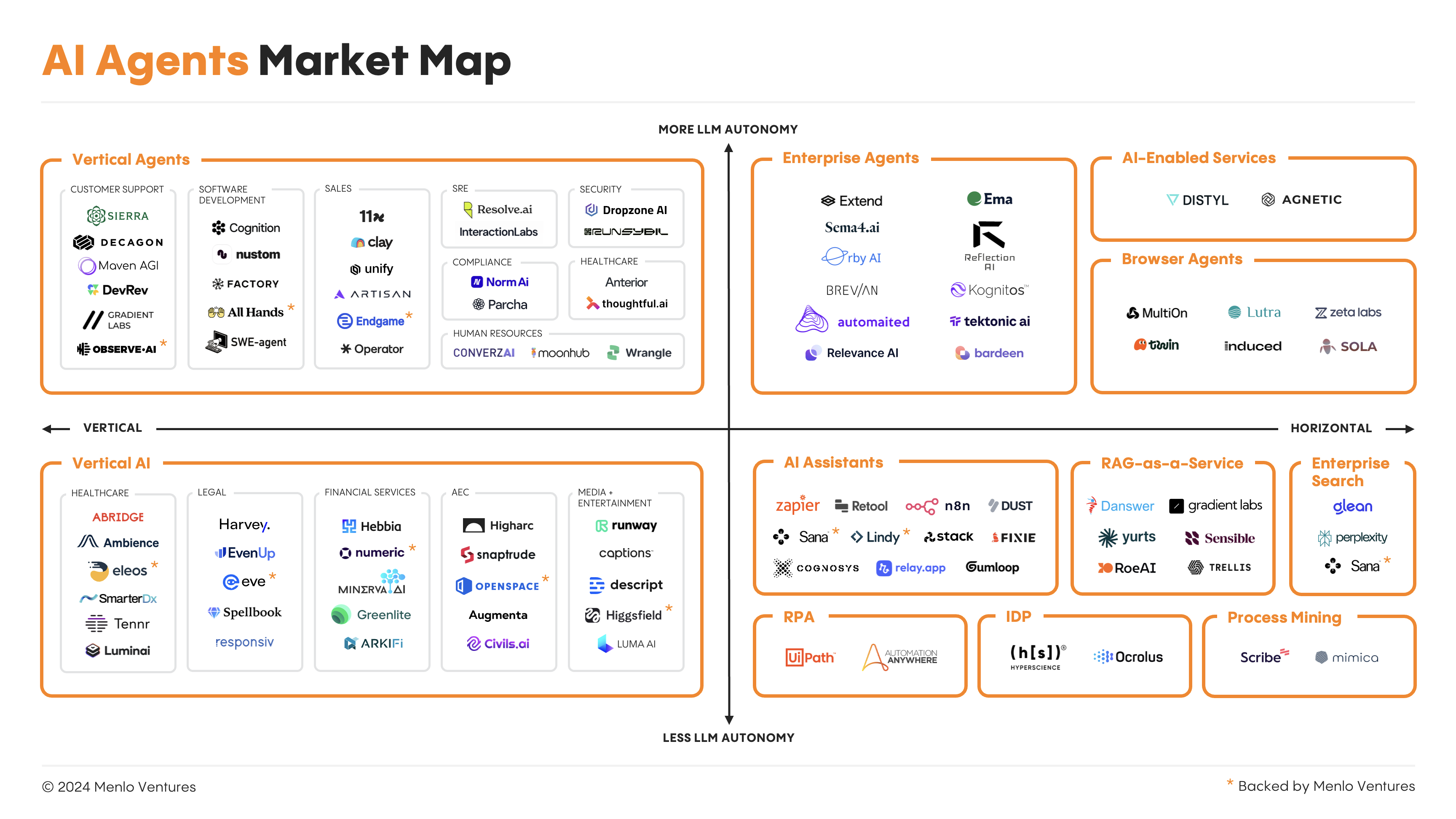
The Shift from Automation to Intelligence
AI agents represent a fundamental paradigm shift. Unlike their predecessors, these systems are not bound by rigid rules or pre-defined workflows. Instead, they possess the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on changing circumstances. This adaptability enables them to address dynamic and complex tasks, unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency and scalability.
However, this evolution introduces a new layer of complexity: agentic security. As AI agents grow more autonomous, ensuring their security, transparency, and trustworthiness becomes paramount, particularly in multi-agent environments where multiple AI systems must collaborate. This shift necessitates rethinking how we secure enterprise automation systems to ensure they remain robust and trustworthy in a rapidly evolving landscape.
The Imperative of Agentic Security
Agentic security involves safeguarding intelligent, autonomous systems while maintaining their transparency and reliability. It becomes especially critical in environments where multiple AI agents operate simultaneously, managing dynamic processes and sensitive data. Key considerations for agentic security include:
Dynamic Adaptability with Robust Security
AI agents excel at adjusting to system changes, but their adaptability must not come at the expense of enterprise security. In multi-agent environments, secure communication protocols and strong authentication mechanisms form the foundation of security. However, static security measures alone are insufficient. Evolving contexts require context-aware security — a system that dynamically adjusts access controls and agent behavior based on situational needs and data sensitivities. This mitigates risks such as unauthorized escalations, prompt injection attacks, and data breaches.
For example, a financial reporting agent, which has access to internal financial metrics, should be able to generate a detailed report for C-suite agents while maintaining strict data boundaries. If an HR agent requests information about salaries, the financial agent should only provide relevant, pre-approved metrics, such as aggregated departmental budgets, rather than individual salary slips. This ensures that agents respect organizational boundaries and adhere to context-aware security protocols.
In cross-enterprise collaborations, where AI agents from different organizations interact, maintaining the integrity of each participant’s systems is essential. Context-aware security ensures that agents respect boundaries and operate within predefined limits, even as they adapt to new information or changing environments.
Transparent Decision-Making and Accountability
As AI agents take on more critical roles in enterprise processes, transparency and accountability become non-negotiable. Organizations must implement mechanisms to trace and audit agent decisions, ensuring they align with business objectives and ethical standards. This is particularly important in regulated industries, where compliance requirements demand a clear understanding of how and why decisions are made.
Trust in Multi-Agent Collaboration
In scenarios where multiple agents collaborate, trust is the cornerstone of effective operation. Agents must communicate securely, share information responsibly, and resolve conflicts without compromising the integrity of the broader system. Establishing trust requires robust encryption, tamper-proof logs, and mechanisms for conflict resolution to prevent unintended behaviors or system failures.
The Path Forward
AI agents represent the next frontier in enterprise automation, promising smarter, faster, and more scalable workflows. However, their increasing sophistication demands a proactive approach to agentic security. As organizations embrace these intelligent systems, they must prioritize building trust, safeguarding data, and ensuring transparency to foster sustainable innovation.
The Menlo Ventures article encapsulates this beautifully: AI agents are not just tools — they are collaborators, reshaping how enterprises operate. But with great power comes great responsibility. By addressing the challenges of agentic security, we can unlock the full potential of AI agents while preserving the integrity and trust that underpin modern enterprises.
Stay in the loop
Get bi-weekly insights on AI agents, SaaS strategy, and the future of software - straight to your inbox.
You're subscribed! Check your inbox soon.
Related Posts
2026: The Year SaaS Disappeared Into the Conversation
SaaS is shifting from dashboards and clicks to personalized, voice-enabled AI agents that execute outcomes. In 2026, the winning software...
OpenClaw and the Rise of User-Built Intelligence: A Wake-Up Call for SaaS
OpenClaw has exploded in popularity with over 114,000 GitHub stars in just two months. It represents a fundamental shift in...
The Agentic Workspace: A Strategic Imperative for the Next Era of SaaS
Traditional SaaS is under siege from AI agents. The winners won't just add AI features—they'll become agentic workspaces that orchestrate...
Context Graphs Are a Trillion-Dollar Opportunity. But Who Actually Captures It?
The concept of Context Graphs has rapidly captured the industry's imagination. The thesis is that the next trillion-dollar enterprise platforms...